DCC
CAS 538-75-0, Cat. No EN300-20280
Reagent for peptide coupling, amide formation, ester, and thioester
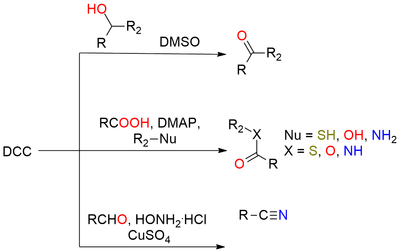
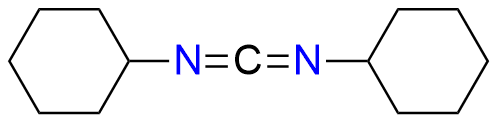
N,N'-dicyclohexylmethanediimine, commonly known as DCC, is a widely recognized reagent extensively used for protein coupling and various amide bond-forming reactions involving primary and secondary amines with carboxylic acids. As a simple carbodiimide reagent, DCC finds numerous applications in diverse fields, including the synthesis of esters and anhydrides. DCC's versatility extends beyond amide bond formation. It can be utilized in conjunction with DMSO for the mild oxidation of alcohols to ketones, and it also plays a role in the dehydrative conversion of primary amides to nitriles, β-hydroxy ketones to α,β-unsaturated ketones, and the stereochemical inversion of secondary alcohols. One of the key advantages of DCC lies in its solubility and low melting point, allowing for easy handling in liquid form.
Synonyms: N,N'-dicyclohexylmethanediimine, Carbodiimide, dicyclohexyl- (6CI, 7CI, 8CI), N,N′-Methanetetraylbis[cyclohexanamine] (ACI), 1,3-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, Bis(cyclohexyl)carbodiimide, Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, DN-TE 9, N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, Cyclohexanamine, N,N′-methanetetraylbis-(9CI, ACI)
Selected publication
1. 1,3-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide.
Albert J. S.; Hamilton A. D.; Hart A. C.; Feng X.; Lin L.; Wang Z. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2017, 1–9. DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rd146
